SET [GLOBAL|SESSION] <variable>
The statement SET [GLOBAL|SESSION] modifies one of TiDB's built in variables, of either SESSION or GLOBAL scope.
Synopsis
SetStmt:
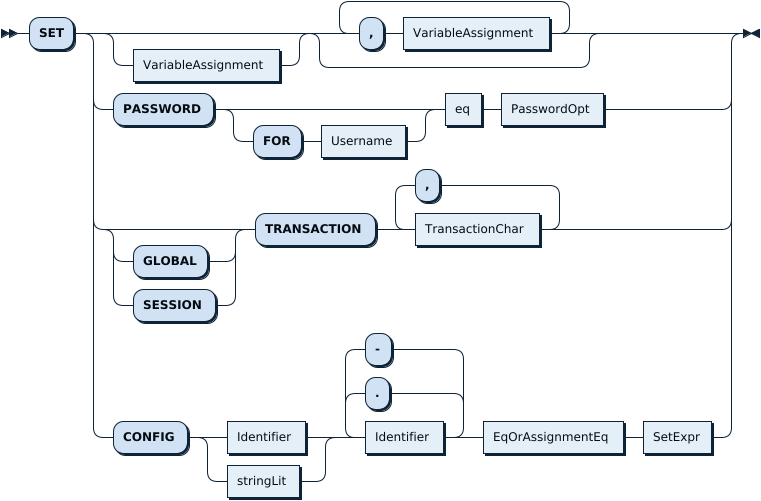
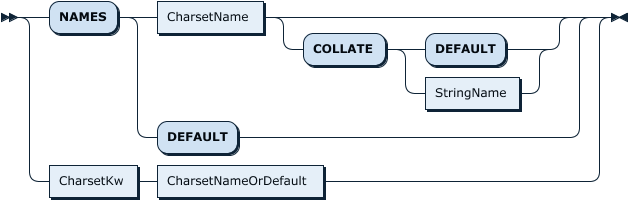
VariableAssignment:
Examples
Get the value of sql_mode.
mysql> SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'sql_mode';
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| sql_mode | ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SHOW SESSION VARIABLES LIKE 'sql_mode';
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| sql_mode | ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Update the value of sql_mode globally. If you check the value of SQL_mode after the update, you can see that the value of SESSION level has not been updated:
mysql> SET GLOBAL sql_mode = 'STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'sql_mode';
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
| sql_mode | STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER |
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SHOW SESSION VARIABLES LIKE 'sql_mode';
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| sql_mode | ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION |
+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Using SET SESSION takes effect immediately:
mysql> SET SESSION sql_mode = 'STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> SHOW SESSION VARIABLES LIKE 'sql_mode';
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
| sql_mode | STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER |
+---------------+-----------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL compatibility
The following behavior differences apply:
- Changes made with
SET GLOBALwill be propagated to all TiDB instances in the cluster. This differs from MySQL, where changes do not propagate to replicas. - TiDB presents several variables as both readable and settable. This is required for MySQL compatibility, because it is common for both applications and connectors to read MySQL variables. For example: JDBC connectors both read and set query cache settings, despite not relying on the behavior.
- Changes made with
SET GLOBALwill persist through TiDB server restarts. This means thatSET GLOBALin TiDB behaves more similar toSET PERSISTas available in MySQL 8.0 and above.
See also
Was this page helpful?